FICO and VantageScore are both measurements of a consumer’s credit score. And while you may be familiar with one or the other, what are the similarities and differences of FICO vs VantageScore? If you’re trying to get out of debt and improve your credit, understanding these distinctions is important.
Paying your credit cards on time – and avoiding credit card debt – is a major factor of your credit score.
FICO vs Vantage Score
To begin, they are competitors. FICO was originally developed by Bill Fair and Earl Isaac in the mid-’50s. VantageScore was developed by the three major credit bureaus; Experian, Equifax, and Transunion in 2006. The whole idea behind credit scores and the importance of them is to be able to measure a consumer’s credit risk. Let’s learn some more about FICO vs VantageScore.
How FICO Works
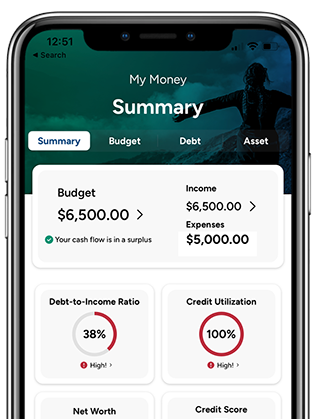
The most common credit scoring system is Fair Isaac Corporation, also known as FICO. FICO was founded to help measure a consumer’s credit risk. To get a FICO score, consumers must have at least one account that has been open for at least six months and at least one other that has already reported to the credit bureau in the last six months. FICO calculates a consumer’s credit score based on 5 credit scoring factors:
- Payment history (35%) – consistent, timely payments make a better score
- Credit utilization (30%) – how much credit a person uses versus how much is available to them
- Length of credit history (15%) – time account has been opened and time since the last action
- New credit (10%) – opening new credit lines
- Credit mix (10%) – repaying debt such as student loan debt shows how a borrower can handle credit
So, for a consumer to improve their credit score, they should consult the scoring factors and evaluate how well they’re complying with FICO’s standards.
How VantageScore Works
Unlike FICO, VantageScore utilizes 6 categories. Each category has a different influence on a consumer’s credit score. VantageScore is able to get a score from one month’s history and an account that that has reported at least once in the last 24 months.
VantageScore prefers not to work in percentages, rather describes their credit factors in terms of influence:
- Payment history: extremely influential
- Age and type of credit: highly influential
- Percentage of credit limit used: highly influential
- Total balances and debt: moderately influential
- Recent credit behavior and inquiries: less influential
- Available credit: less influential
With either score, the biggest impact, and the most important thing consumers can do is pay on time.
If you’re struggling to pay off debt, ACCC can help. Schedule a free credit counseling session with us today.